Forgetting passwords is a common problem that often plagues users when they try to log in to their favorite application or website. As well as causing frustration, frequently changing passwords can also negatively impact account security.
But is there a solution to this dilemma without compromising security? The answer is a single sign-on (SSO) system. Although this term may still sound unfamiliar to some people, SSO has great potential to change the way we interact with various digital platforms. So what exactly is SSO and how does it work? Read this article for the full explanation.
What is Single Sign On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication mechanism that allows users to access multiple applications or systems using a single set of credentials (such as a username and password) only once when they log in.
In other words, SSO allows users to log in to multiple systems or applications with a single authentication process. Once a user logs in, SSO provides an authentication token that can be used to access other systems without having to log in again.
The concept of SSO is very important in the modern IT environment because it can improve productivity and security. With SSO, users don’t have to remember multiple credentials for each system or application they use, which can reduce login errors and speed up the access process. In addition, SSO can improve security by reducing the risk of weak or stolen credentials, as users only need to enter their credentials once.
6 Benefits of SSO

Here are six benefits of Single Sign-On (SSO):
1. User Convenience
Enables users to access various applications and services with a single authentication process. This reduces the number of logins a user must remember and enter.
2. Higher Productivity
Users don’t have to spend time logging in and out of various applications. This saves time and increases productivity.
3. Enhanced Security
While it may sound paradoxical, SSO can improve security. By only needing to remember one login credential, users tend to choose stronger passwords.
4. Reducing IT Burden
IT teams no longer need to handle many password resets performed by users who have forgotten their passwords, because users only need to reset one credential.
5. Easy Integration
Integrates with multiple applications and systems, both cloud-based and on-premises. This makes it easier to manage and use multiple services in a complex environment.
6. Better Compliance and Audit
User activity can be better tracked. This makes it easier for companies to comply with compliance regulations and conduct audits of user access.
Also read: Prepare Your Business: The PDP Act Has Passed – Key Steps for Compliance!
How Does SSO Work?
The way Single Sign-On (SSO) works involves several entities and steps, generally involving an identity provider (IdP), a service provider (SP), and an end user. Here are the general steps in how SSO works.
Access Request
The user tries to access a specific application or system that is protected by SSO.
Redirect to Identity Provider (IdP)
The SP detects that the user has not been authenticated and redirects the user to the IdP.
User Authentication
In the IdP, users are asked to enter their credentials (for example, username and password).
Authentication by IdP
The IdP validates the credentials provided by the user. If successful, the IdP generates an authentication token or access token stating that the user has been authenticated.
Return Authentication Token to SP
After successful authentication, the IdP sends an authentication token to the SP.
Token Verification by SP
The SP verifies the authentication token received from the IdP to ensure its authenticity.
User Allowed Access
If the authentication token is valid, the user is permitted to access the requested application or system.
Active Session
During an active session, users do not need to re-enter their credentials when accessing applications or other systems protected by SSO. They can access it automatically using the authentication token that the SP has received.
What are the Types of SSO?
There are several different types of SSO (Single Sign-On), depending on how it works and the usage scenario. Here are some common SSO types.
Enterprise SSO (ESSO)
Enables users to access various applications in an enterprise environment with a single authentication process.
Typically used within enterprises to provide access to internal and external applications, users only need to enter their credentials once, and then they can access all permitted applications without needing to log in again.
Web SSO
Web SSO is the most common type of SSO, where users only need to log in once to access various websites or web applications. Typically used in the internet environment to provide access to various web services.
Federated SSO
Enables users to access services from multiple domains with a single authentication process. Typically used between companies or entities that are separate but have a business relationship or partnership.
Mobile SSO
Allows users to log in to mobile applications with a one-time authentication process. Typically used in mobile applications to provide an easier login experience to users.
Desktop SSO
Enables users to access desktop applications with a single authentication process. Typically used within enterprise environments to provide access to desktop applications.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of SSO?
Advantages
- Ease of Use
Reduce the burden on users by allowing them to sign in to multiple applications with a single authentication process.
- High Productivity
Eliminating the need to enter credentials multiple times, SSO increases user productivity.
- Reducing Credential Management Burden
IT administrators can manage user access centrally, reducing complexity in credential management.
- Better Security
Users often have a habit of using the same or weak passwords for several applications.
- Better Access Monitoring
IT managers can more easily monitor and analyze user access activity with SSO because access is consolidated.
Disadvantages
- Single Point of Failure
If SSO is compromised or vulnerable to attack, access to applications could be disrupted altogether.
- Centralized Security
While SSO can improve security by reducing the risk of weak credentials, if someone gains access to the SSO master credentials, they can access all connected applications.
- Dependency on Identity Providers
If the identity provider experiences problems or disruptions, access to related applications may also be affected.
- Application Updates
SSO integration with existing applications may require additional effort, especially if the application does not support standard SSO protocols.
- Complicated Integration
Implementing SSO in a complex IT environment can require complex integration with existing infrastructure.
Is SSO Safe?
SSO can be secure if implemented well and managed carefully. Proper SSO protocols, correct configuration, and strict security practices are necessary to ensure SSO security.
However, as with many security technologies, no security solution is perfect. Some security risks that need to be considered in implementing SSO include:
Primary Credential Compromise
If SSO master credentials are stolen, an attacker can access all applications connected to SSO.
Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) Attacks
MITM attacks can cause sensitive authentication information to be stolen during communications between users, identity providers, and service providers.
Service Interruption
SSO is vulnerable to service disruptions that can hinder user access to various applications if the SSO infrastructure experiences problems.
Risk of Unintentional Changes
Incorrect SSO configuration or unintentional changes in configuration can result in security vulnerabilities.
Read more: What is Zero Trust Security and Its Benefits for Your Business Security?
With the right approach, SSO can be a powerful tool for improving security and productivity in an IT environment. To answer these challenges, you can use several SSO solutions from CDT such as AWS IAM Identity Center, Zscaler Private Access (ZPA), and Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA) to guarantee strong encryption, strict access control, and monitoring of user activity.
Recommendations for Several Solutions to Support Application and Website SSO from CDT
Central Data Technology (CDT) presents several solutions that can support Single Sign-On (SSO) securely. Here are three solutions you can integrate to support a secure SSO implementation.
AWS IAM Identity Center
AWS IAM Identity Center is a managed Single Sign-On (SSO) service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). This service is designed to provide centralized authentication and authorization for access to various AWS services and third-party applications.
Additionally, AWS IAM Identity Center allows users to access multiple services with a single sign-in using the same credentials.
Main feature:
- Allows access to various services with a single sign-in
- Manage user access rights efficiently and centrally
Benefit
- Uses AWS security standards to protect user access
- Increase productivity with easy and fast access
- Integrates directly with the AWS ecosystem, ensuring efficient and secure access management
Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) is a Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) service that provides secure, managed access to internal and SaaS (Software as a Service) applications from anywhere and at any time.
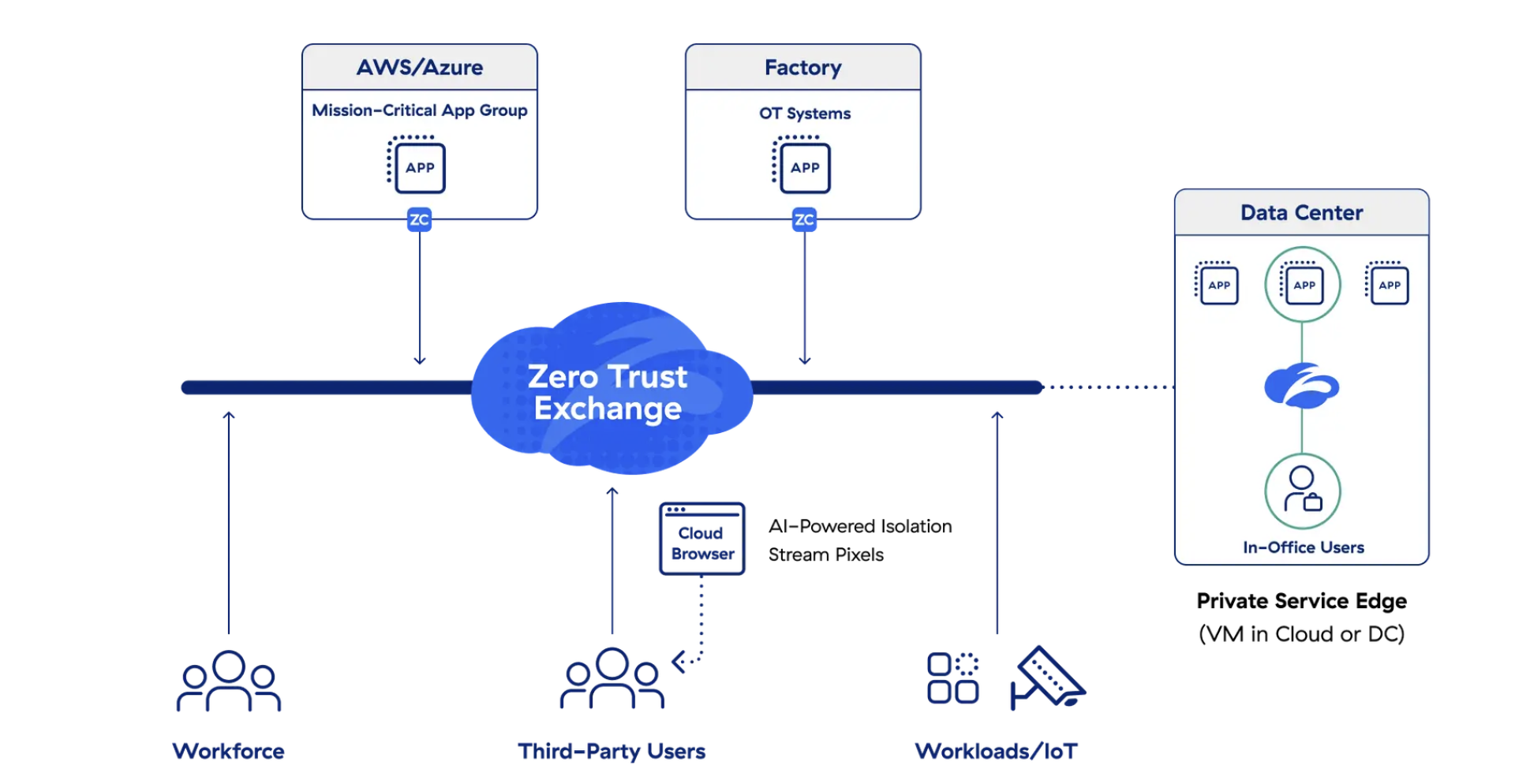
Source: Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
ZPA applies a zero-trust approach, meaning that user access to applications and data is decided based on identity and context, not based on location or network infrastructure.
Main feature:
- Enables secure access to internal and SaaS applications from anywhere, without going through a VPN
- Zero-trust principles to secure access by validating device identity and condition
- Support Single Sign-On (SSO) through identity provider integration and centralized access management
- Protect applications and data from cyberattacks with traffic filtering and strict security policies
Benefit:
- Access applications and data from anywhere and at any time
- Administrators can manage user access and security policies centrally
- Reduce network infrastructure complexity and costs associated with using a VPN Good visibility into user activity and perform thorough audits
Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA)
Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA) is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG) service designed to protect users and devices from cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and other malicious threats.
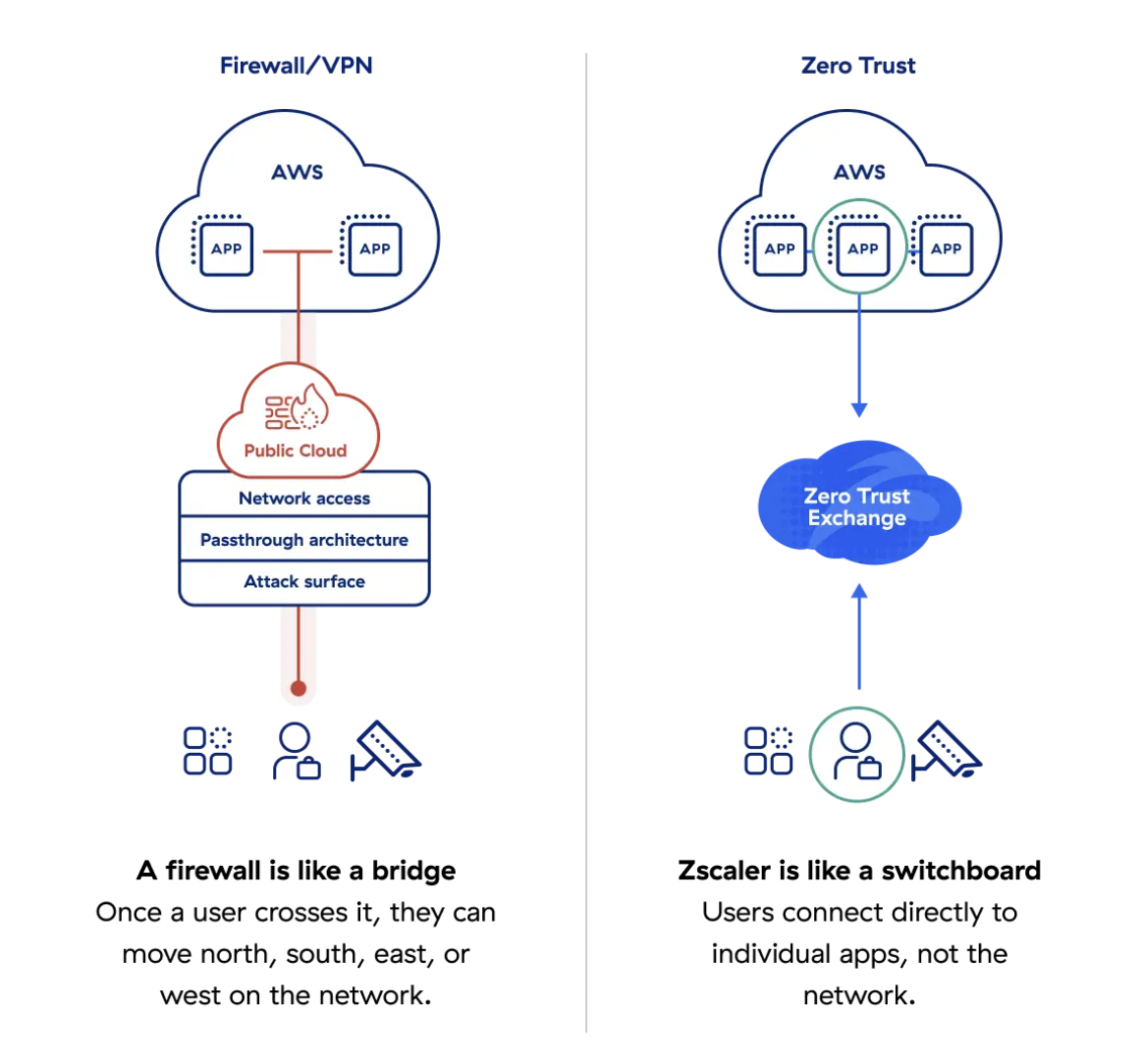
Source: Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA)
This service provides high security and sophisticated internet access control for users inside and outside the corporate network.
Main feature:
- Prevent access to dangerous websites by detecting and removing malware
- Granular control over internet content accessed by users
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) traffic analysis for hidden threat detection
- Complete visibility into user activity and internet threats through in-depth reporting and analysis
- Support Single Sign-On (SSO) through integration with multiple identity providers
Benefit:
- Protect users and devices from malware and phishing threats
- Optimize internet performance and reduce the risk of service interruptions
- Reduce infrastructure complexity and costs
- Good visibility into user internet activity and thorough auditing
Overall, by integrating AWS IAM Identity Center, ZPA, and ZIA as an SSO solution, companies can ensure that user access to internal applications and the internet is secure, efficient, and convenient.
Get Integrated and Secure SSO Solutions Only at CDT
Deliver an advanced Single Sign-On (SSO) system throughout your company’s digital ecosystem to increase security and prevent forgotten passwords through an integrated SSO solution from AWS IAM Identity Center, Zscaler Private Access (ZPA), and Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA) only at Central Data Technology (CDT).
For further information regarding implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions from AWS and Zscaler in your business, don’t hesitate to contact us by clicking the following link.
Author: Ary Adianto
CTI Group Content Writers