During increasing digitalization, observability is crucial for businesses because it will make it easier to understand system performance, even in complex systems such as microservices architectures and cloud infrastructure.
Observability allows businesses to track, analyze and respond to changes or problems quickly and efficiently. Without observability, companies will have difficulty identifying the source of problems, finding bottlenecks in infrastructure, or understanding the impact of the changes they make.
So, why is observability an important foundation in maintaining system availability, reliability and performance in an increasingly complex and rapidly changing digital infrastructure? Find the answer in this article.
What is Observability?
Observability is the ability to understand, analyze, and observe how a system works from the inside. In the context of modern business, observability means having broad and deep visibility into the performance of computer systems and software that support business operations. This includes monitoring application performance, IT infrastructure, communications networks, and customer service.
With observability, the company’s technical team can quickly identify problems, analyze the root causes, and take appropriate action to improve system performance and availability. This, in turn, will enhance user experience and optimize business operations across the board.
How Does Observability Work?
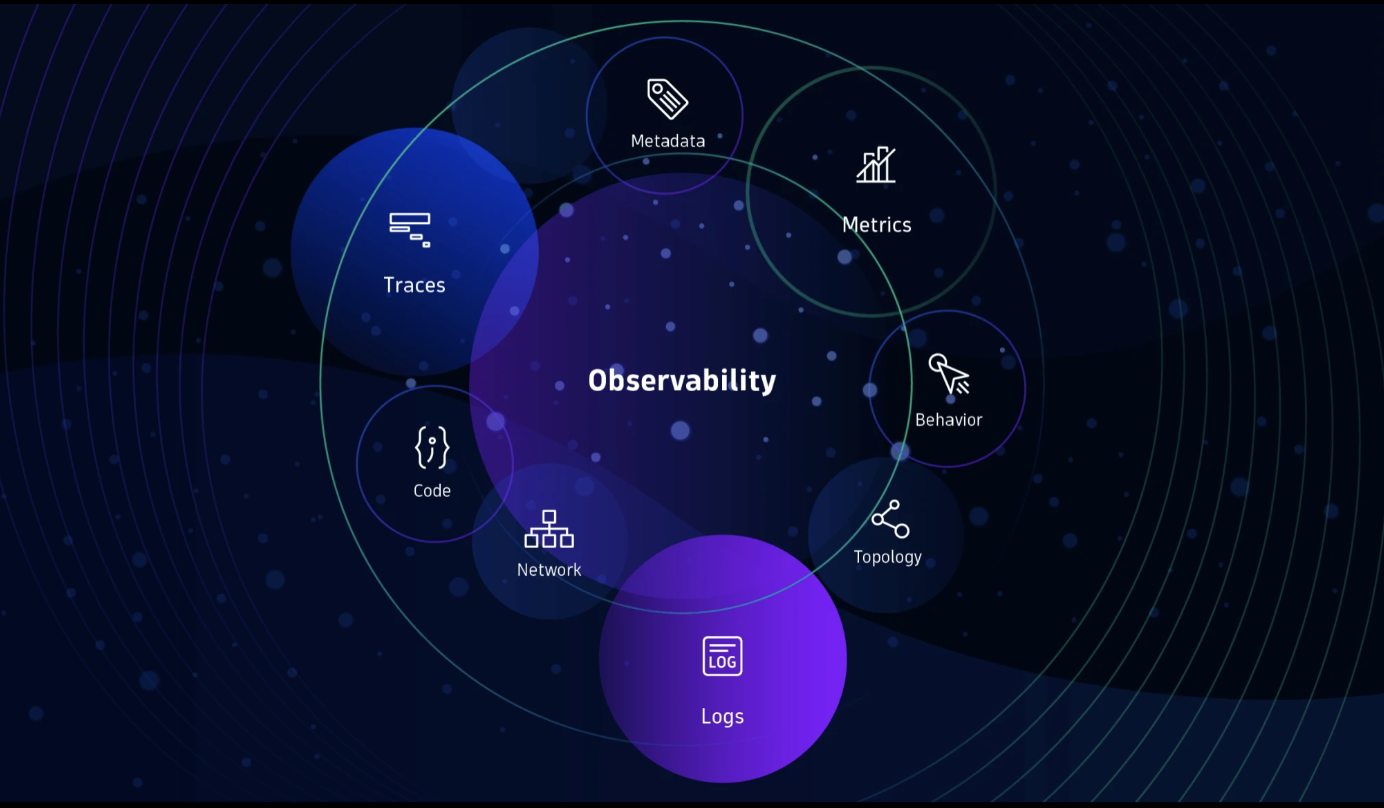
Source: dynatrace.com
Observability works involves collecting, storing, analyzing, and interpreting data generated by various components in a system. Here are the steps for how observability works:
Data Collection
Observability begins with collecting data from various sources in the system. This includes logs, metrics, traces, and other information generated by components such as applications, infrastructure, or networks.
Data Storage
The collected data is then stored in a storage system designed to handle Big Data allowing fast and efficient access for subsequent analysis.
Data Analysis
After the data is saved, the next step is to analyze the data to gain insight. This involves using data analysis algorithms, visualization, and other techniques to identify patterns, trends, anomalies, or potential problems in system performance.
Data Interpretation
One important aspect of observability is the interpretation of the data analyzed. IT professionals need to understand the meaning behind the data presented, identify root-causes, and formulate necessary actions to improve performance or fix detected problems.
By following these steps, observability allows companies to gain a better understanding of overall system performance and quickly respond to changes or problems.
But did you know, observability is often equated with monitoring, even though the two have significant differences. So, what’s the difference? The following is the explanation.
Observability vs Monitoring, Same or Different? This is the explanation
Observability is often equated with monitoring, but the two have significant differences. Some of the differences include:
- Monitoring tends to focus on measuring performance and detecting problems by using metrics, log monitoring, tracing, and alerts to notify when unwanted events occur. On the other hand, observability focuses more on a deep understanding of system behavior through data generated by its various components.
- Monitoring is more focused on reactive responses to abnormal system behavior, while observability emphasizes proactive understanding. Observability allows users not only to detect problems but also to understand why they occurred and how to resolve them.
- Monitoring focuses on known metrics (known known), such as application throughput and pre-defined computational capacity. Meanwhile, observability enables the discovery of previously unknown aspects (unknown unknowns) in complex systems like microservices and distributed systems. This includes allowing users to discover patterns, trends, and relationships among components that are not clearly visible through monitoring alone.
5 Challenges of Implementing Observability

Although observability is key to understanding overall system performance, there are challenges that must be overcome to implement it effectively.
1. Infrastructure Complexity
Modern IT environments are often highly complex, consisting of a wide variety of technologies, platforms, and architectures such as microservices, cloud, and containers. This makes collecting, analyzing and understanding data more complicated.
2. Data Volume and Diversity
Complex systems generate large and varied volumes of data. The main challenge is managing data at scale and identifying relevant and meaningful information amidst data noise.
3. Integration and Interoperability
Bringing together data from various sources and technologies is a challenge. Ensuring interoperability between various monitoring systems and analysis tools is crucial to getting a complete picture.
4. New Skills Needed
Managing complex systems and big data requires new skills such as data analysis, programming, and infrastructure management. This challenge requires efforts in developing team skills or finding suitable new talent.
5. Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and compliance in an observability environment is a critical challenge. Management of sensitive data and user privacy is a major concern in the context of data collection and analysis.
To overcome these challenges, holistic and coordinated solutions are needed, for example the Observability infrastructure solution from Dynatrace which can be relied on to carry out comprehensive analysis and visibility of IT infrastructure, so that it can improve the performance, availability and security of the company’s IT systems.
About Dynatrace’s Observability Infrastructure
Dynatrace Infrastructure Observability is the ability of the Dynatrace platform to provide comprehensive and in-depth insight into the performance and state of a company’s IT infrastructure.
Using a variety of monitoring technologies including AI and Machine Learning, Dynatrace can automatically collect, analyze and understand data from various infrastructure sources such as servers, networks, cloud and managed services. This enables IT teams to proactively detect problems, identify root causes, and optimize infrastructure performance efficiently.
One of the superior features of Dynatrace infrastructure observability is its ability to provide end-to-end visibility into complex infrastructure environments. Equipped with in-depth real-time monitoring, Dynatrace can provide accurate information about the performance of each infrastructure component, as well as identify anomalous behavior patterns that could indicate problems or potential risks.
Additionally, the platform also comes with cloud-native monitoring features that enable companies to gain better insight into the performance of applications and services running in cloud environments such as Kubernetes and AWS.
With Dynatrace, companies can certainly increase operational responsibility, reduce downtime, and improve the end user experience. Additionally, by having a better understanding of the performance of their infrastructure, companies can make more timely and effective decisions in managing and optimizing their overall IT environment.
5 Benefits of Dynatrace Infrastructure Observability
Here are five benefits of Dynatrace’s observability infrastructure:
1. Efficient Root Cause Analysis
Combine, store, and analyze large amounts of contextual infrastructure data with speed and cost efficiency using a data lakehouse.
2. Increase Efficiency and Productivity
Equipped with AI technology that continuously monitors all your infrastructure to detect anomalies and provide the right answers for business continuity.
3. Customized Log Metrics
Extend infrastructure observations to everything logged in log files with custom metrics based on log data.
4. An Integrated Approach to Eliminate Silos
Dynatrace Infrastructure Monitoring provides a unified view across the entire chain, from applications, infrastructure, to user experience. Supported by AI and Davis, companies can continuously analyze billions of dependencies for precise root cause analysis.
5. Efficient Incident Management Automation
Integrates seamlessly with ITSM solutions like ServiceNow, enabling real-time CMDB updates, automated ticketing, and running remediation workflows automatically.
Implement Dynatrace Observability Only in CDT
Deliver advanced observability across PaaS and container technologies, including AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Cloud Foundry by deploying Observability Dynatrace only on CDT. This includes real-time monitoring, trending analysis, the ability to perform root cause and correlation analysis, log monitoring and third-party data integration.
For further information regarding implementing the Observability solution from Dynatrace in your business, don’t hesitate to contact us by clicking the following link.
Author: Ary Adianto
CTI Group Content Writers